Technical SEO is the backbone of any successful search engine optimization strategy. It’s the process of optimizing a website’s technical aspects to improve its visibility on search engines.
In today’s competitive digital landscape, mastering technical SEO is no longer optional. It is a critical component for any website owner or web developer looking to improve their site’s visibility in search engines, drive organic traffic, and achieve online success. This comprehensive guide will provide you with the essential knowledge, tips, and strategies to optimize your website’s technical aspects, ensuring a solid foundation for your search engine optimization efforts.
Crawling, Indexing, and Rendering

What is Crawling?
Crawling is the process by which search engines like Google discover new and updated content on your website. This is done using automated bots known as crawlers or spiders. They follow links from one webpage to another, gathering information about your content and storing it in their databases.
What is Indexing?
Indexing is the next step after crawling. Once search engines have discovered your content, they analyze and store it in their databases or “indexes.” When users perform a search query, search engines use their indexes to find the most relevant content and display it in the search results.
What is Rendering?
Rendering refers to how search engines process and display your website’s content in the search results. This process involves converting your HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and other resources into a visual representation that users can see and interact with.
Strategies for Improving Crawling, Indexing, and Rendering
- Create a clear and logical site structure: A well-organized site structure makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content. This includes using relevant headings, subheadings, and internal links to guide crawlers through your website.
- Optimize your website’s crawlability: Ensure that all your important pages are accessible and not blocked by your robots.txt file. Also, avoid using AJAX, Flash, or other technologies that may hinder search engines from crawling your content.
- Improve page load times: Fast-loading pages are more likely to be crawled, indexed, and rendered quickly by search engines. Optimize your images, minimize HTTP requests, and utilize caching to speed up your website.
- Submit your XML sitemap: Create and submit an XML sitemap to search engines, providing a roadmap of your site’s content and guiding crawlers to your most important pages.
Keep your website’s content up to date: Regularly update your website with fresh, relevant content, signaling to search engines that your site is active and worth indexing.
Site Architecture and URL Structure
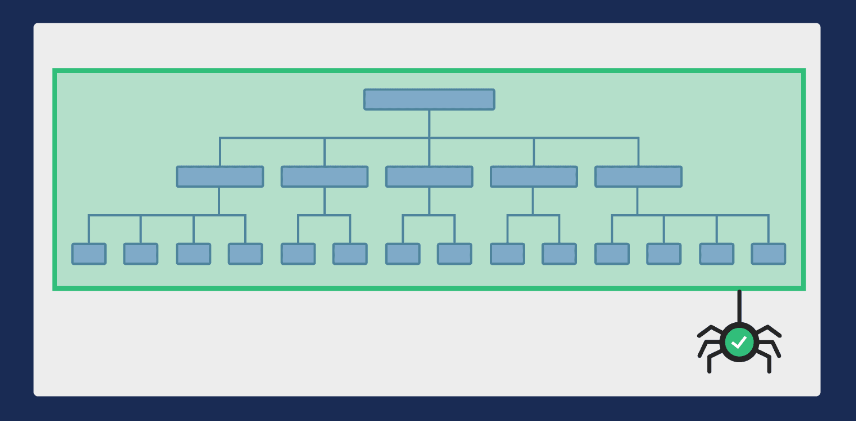
What is Site Architecture?
Site architecture refers to the organization and structure of your website’s content. A well-designed site architecture not only enhances the user experience but also makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index your website. An effective site architecture should be logical, easy to navigate, and scalable.
What is URL Structure?
URL structure refers to the format and organization of your website’s URLs. A clean, descriptive, and logical URL structure is important for both search engines and users. A well-structured URL should be easy to read, include relevant keywords, and accurately represent the content of the page.
Strategies for Improving Site Architecture and URL Structure
- Use descriptive and keyword-rich URLs: Include relevant keywords in your URLs to help search engines understand your content better. Keep URLs simple, descriptive, and easy to read.
- Implement a flat site hierarchy: A flat site hierarchy helps search engines crawl and index your website more efficiently. Aim for a shallow structure with a limited number of clicks required to reach any page on your site.
- Organize content into categories and subcategories: Group related content together under appropriate categories and subcategories, making it easier for both users and search engines to find and navigate your content.
- Utilize breadcrumb navigation: Breadcrumb navigation provides users with a clear path to follow, helping them understand their position on your site. It also benefits SEO by providing additional internal links and improving crawlability.
- Optimize internal linking: Use internal links to guide search engines and users through your website, connecting related content and distributing link equity across your site.
Redirects, Canonical Tags, and Duplicate Content
What are Redirects?
Redirects are instructions that automatically guide users and search engines from one URL to another. They are essential for maintaining a user-friendly website and ensuring search engines can efficiently crawl your site. There are several types of redirects, with the most common being 301 (permanent) and 302 (temporary) redirects.
What are Canonical Tags?
Canonical tags are HTML elements used to indicate the preferred version of a webpage when multiple versions with similar or duplicate content exist. By adding a canonical tag to a page, you signal to search engines which version should be indexed and considered the authoritative source.
What is Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content refers to similar or identical content that appears on multiple pages or websites. Duplicate content can cause confusion for search engines, resulting in lower rankings or penalties. Addressing duplicate content issues is crucial for maintaining a search engine-friendly website.
Strategies for Managing Redirects, Canonical Tags, and Duplicate Content
- Use 301 redirects for permanent changes: When moving or deleting content, use 301 redirects to guide users and search engines to the updated page or a relevant alternative.
- Implement canonical tags for duplicate content: When multiple versions of a page exist, use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version for search engines to index.
- Consolidate similar content: If you have multiple pages with similar or duplicate content, consider consolidating them into a single, comprehensive page to avoid search engine penalties.
- Monitor for duplicate content: Regularly audit your website for duplicate content issues, using tools like Copyscape or Google Search Console, and address any issues you find.
XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt
What are XML Sitemaps?
XML sitemaps are files that provide a roadmap of your website’s content, helping search engines efficiently crawl and index your site. They list your website’s URLs, along with metadata such as the last modification date and priority, guiding search engines to your most important content.
What is Robots.txt?
A robots.txt file is a text file placed in your website’s root directory, which provides instructions to search engine crawlers about which pages or sections of your website should be crawled and indexed. Properly configured robots.txt files help search engines prioritize their crawling and indexing efforts, ensuring that your most important content is indexed.
Strategies for Optimizing XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt
- Create and submit an XML sitemap: Generate an XML sitemap that includes all your important pages, and submit it to search engines using tools like Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Update your XML sitemap regularly: Keep your XML sitemap up-to-date by adding new pages and removing deleted ones. Regularly updating your sitemap ensures search engines have the most recent information about your website’s content.
- Organize your XML sitemap: Group related pages together in your sitemap, and prioritize them based on their importance. This helps search engines understand your site’s structure and index your content more efficiently.
- Optimize your robots.txt file: Use your robots.txt file to provide clear instructions to search engines about which pages or sections of your website should be crawled and indexed. Be cautious when blocking content, as it may impact your site’s visibility in search results.
- Test your robots.txt file: Use tools like Google’s robots.txt Tester to ensure your file is properly formatted and doesn’t contain errors that could impact search engine crawling.
Website Speed and Mobile Optimization
Why is Website Speed Important?
Website speed is a crucial ranking factor for search engines. Faster-loading websites provide a better user experience and are more likely to rank higher in search results. Slow-loading websites can lead to higher bounce rates, lower conversion rates, and a negative impact on your website’s overall performance.
What is Mobile Optimization?
Mobile optimization involves designing and developing your website to ensure it is easily accessible, navigable, and functional on mobile devices. With the growing number of mobile users worldwide, mobile optimization has become a crucial aspect of Technical SEO.
Strategies for Improving Website Speed and Mobile Optimization
- Optimize images: Compress and resize images to reduce their file size without compromising quality. Use appropriate image formats, such as WebP or JPEG, for better performance.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Minify your code by removing whitespace, comments, and unnecessary characters to reduce file sizes and improve page load times.
- Leverage browser caching: Enable browser caching to store static files on users’ devices, reducing the need for repeated requests to your server and improving load times.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN): Distribute your content across multiple servers worldwide using a CDN to reduce latency and improve page load times for users in different locations.
- Implement responsive design: Use a responsive design approach to ensure your website automatically adapts to different screen sizes and orientations, providing an optimal user experience on all devices.
- Test your website on various devices: Regularly test your website on different mobile devices and browsers to identify and fix any performance or usability issues.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
What is Structured Data?
Structured data is a standardized format for providing information about your website to search engines. By adding structured data to your pages, you help search engines understand your content and display it in more informative and attractive ways in the search results.
What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a specific type of structured data that uses a standardized vocabulary to describe your content to search engines. Implementing schema markup helps search engines understand your content’s context and display rich snippets, such as star ratings or event details, in the search results.
Strategies for Implementing Structured Data and Schema Markup
- Choose the most appropriate schema types: Identify the most relevant schema types for your website’s content, such as articles, products, or events, and implement them accordingly.
- Use structured data testing tools: Use tools like Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool or the Schema Markup Validator to test your structured data implementation and ensure it is properly formatted and error-free.
- Keep your structured data up-to-date: Regularly review and update your structured data to ensure it accurately represents your content and provides the most current information to search engines.
- Avoid spammy markup: Be cautious not to over-optimize your structured data or include misleading information, as this could lead to penalties from search engines.
- Leverage JSON-LD: Use JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) as the preferred format for implementing schema markup, as it is easy to implement and recommended by Google.
HTTPS and Security
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is an encrypted version of HTTP, the protocol used to transfer data between your website and users’ browsers. HTTPS adds a layer of security, protecting your website and its users from potential attacks, data theft, and unauthorized access.
Why is HTTPS Important for SEO?
HTTPS is important for SEO because search engines, especially Google, consider it a ranking factor. A secure website provides a better user experience and is more likely to rank higher in search results. Additionally, HTTPS is essential for building trust with your users, as browsers display a security warning for non-HTTPS websites.
Strategies for Implementing HTTPS and Improving Security
- Obtain an SSL/TLS certificate: Acquire an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) certificate from a reputable certificate authority and install it on your server to enable HTTPS on your website.
- Redirect HTTP to HTTPS: Ensure that all HTTP traffic is redirected to HTTPS, so users and search engines always access the secure version of your website.
- Update internal and external links: Update all internal and external links to use HTTPS, avoiding mixed content issues and ensuring a secure browsing experience.
- Monitor your website’s security: Regularly review your website’s security settings, monitor for potential vulnerabilities, and promptly address any issues to maintain a secure website.
Broken Links, Site Migrations, and Crawl Budget
What are Broken Links?
Broken links are links that lead to non-existent or inaccessible pages, resulting in a 404 error. Broken links negatively impact the user experience and hinder search engine crawling, potentially harming your website’s SEO performance.
What are Site Migrations?
Site migrations are significant changes to your website’s structure, content, design, or platform that can impact its visibility in search results. Examples of site migrations include moving from HTTP to HTTPS, changing domain names, or redesigning your website.
What is Crawl Budget?
Crawl budget refers to the number of pages a search engine is willing to crawl on your website within a given time frame. Optimizing your crawl budget ensures that search engines efficiently index your most important content, improving your website’s overall SEO performance.
Strategies for Managing Broken Links, Site Migrations, and Crawl Budget
- Regularly audit your website for broken links: Use tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to identify broken links on your website, and fix them by updating the URL or implementing redirects.
- Plan and monitor site migrations: Carefully plan and execute site migrations to minimize potential SEO issues. Monitor your website’s performance and rankings during and after the migration to identify and address any problems.
- Optimize your crawl budget: Improve your crawl budget by eliminating duplicate content, blocking low-value pages using robots.txt, and ensuring your website loads quickly. This will help search engines focus on indexing your most important content.
- Leverage XML sitemaps and internal linking: Use XML sitemaps and internal linking to guide search engines to your most important content, ensuring efficient crawling and indexing.
- Monitor your website’s crawl stats: Regularly review your website’s crawl stats in Google Search Console to identify potential issues affecting crawl budget and address them promptly.
Log File Analysis, International SEO, and Hreflang Tags
What is Log File Analysis?
Log file analysis is the process of examining your website’s server logs to gain insights into how search engine crawlers interact with your site. This data can be used to identify issues impacting crawlability, optimize your crawl budget, and improve your website’s overall SEO performance.
What is International SEO?
International SEO involves optimizing your website for users in different countries and languages. This includes implementing strategies such as geo-targeting, multilingual content, and the use of hreflang tags to ensure your website ranks well in search results for users worldwide.
What are Hreflang Tags?
Hreflang tags are HTML tags used to indicate the language and regional targeting of a webpage. They help search engines understand which language versions of a page to display in search results, ensuring that users see content in their preferred language.
Strategies for Log File Analysis, International SEO, and Hreflang Tags
- Analyze your log files: Regularly review your server logs to identify how search engine crawlers interact with your website, and use this data to optimize your crawl budget and address any issues.
- Target your international audience: Determine your target audience based on geographic location and language preferences, and create content tailored to their needs.
- Implement hreflang tags: Use hreflang tags on multilingual websites to signal the language and regional targeting of each page to search engines, ensuring users see the appropriate content in search results.
- Leverage geo-targeting: Use tools like Google Search Console to set geo-targeting preferences for your website, ensuring it ranks well for users in specific countries or regions.
- Optimize your website’s language and regional settings: Use language-specific URLs, meta tags, and other on-page elements to clearly indicate your website’s language and regional targeting to search engines.
Pagination, JavaScript SEO, and Social Media Tags
What is Pagination?
Pagination is the process of dividing content into smaller, more manageable sections or pages. Pagination is commonly used on websites with large amounts of content, such as e-commerce sites or blogs, to improve the user experience and facilitate search engine crawling.
What is JavaScript SEO?
JavaScript SEO involves optimizing your website’s JavaScript code to ensure that search engines can effectively crawl, index, and render your content. As search engines have evolved to better understand JavaScript, it has become increasingly important to optimize your JavaScript code for SEO.
What are Social Media Tags?
Social media tags are HTML tags that provide information about your website’s content to social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. These tags help control how your content is displayed when shared on social media, ensuring a consistent and attractive presentation.
Strategies for Pagination, JavaScript SEO, and Social Media Tags
- Implement best practices for pagination: Use appropriate pagination techniques, such as rel=”next” and rel=”prev” tags or the “load more” button, to ensure search engines can efficiently crawl and index your paginated content.
- Optimize your JavaScript code: Minimize your JavaScript code, use progressive enhancement techniques, and ensure your website’s content is accessible even when JavaScript is disabled. This will help search engines effectively crawl, index, and render your content.
- Leverage server-side rendering (SSR) or dynamic rendering: Utilize server-side rendering or dynamic rendering to serve a pre-rendered version of your content to search engines, ensuring your JavaScript-heavy content is indexed and ranked properly.
- Test your website’s JavaScript SEO: Regularly test your website’s JavaScript SEO using tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test or the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to identify and address any issues.
- Implement social media tags: Use social media tags such as Open Graph tags (for Facebook and LinkedIn) and Twitter Card tags to control how your content is displayed when shared on social media platforms, improving its attractiveness and shareability.
- Monitor your social media performance: Regularly review your social media performance and engagement metrics to identify trends and opportunities for improvement.
Wrapping It Up
Technical SEO is a critical aspect of search engine optimization that ensures your website’s foundation is strong, allowing your content and marketing efforts to reach their full potential. By addressing the various elements discussed in this guide, you’ll create a website that is more accessible, user-friendly, and attractive to both users and search engines. Stay up-to-date with best practices and industry trends, regularly audit your website, and continuously improve your technical SEO to achieve and maintain high rankings in search results.

